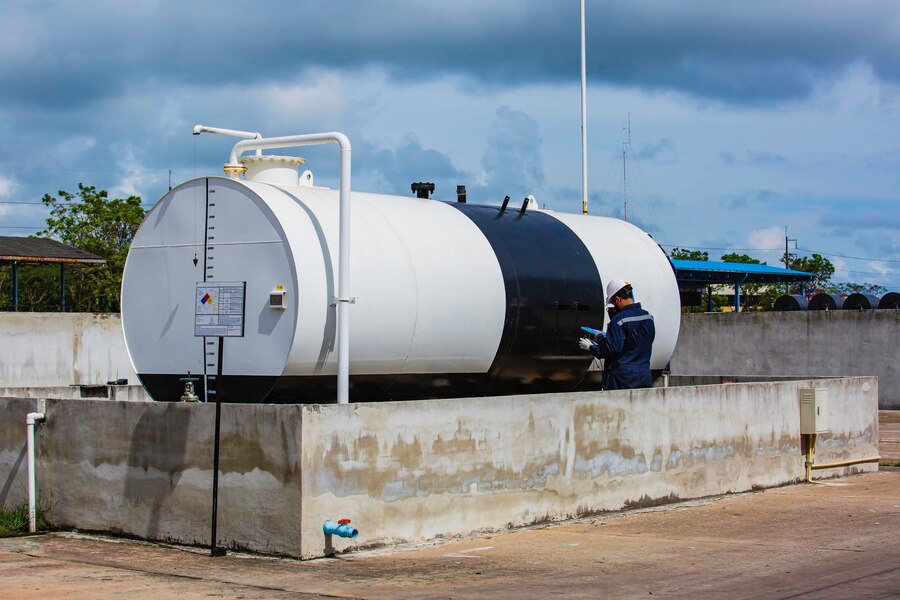
A 1000 gallon fuel tank is a versatile and essential storage solution for various industries requiring bulk fuel storage. Whether for agriculture, commercial operations, or backup power generation, these tanks provide a reliable way to store significant amounts of fuel safely and efficiently. This article explores the features, types, benefits, regulations, and maintenance tips for a 1000 gallon fuel tank.
Types of 1000 Gallon Fuel Tanks
Fuel tanks come in various designs and materials to suit different needs. The primary types include:
- Above-Ground Fuel Tanks (AGT): Commonly used in commercial settings, AGTs are easier to install and inspect but may be more vulnerable to environmental elements.
- Underground Fuel Tanks (UGT): Designed for minimal visibility and space efficiency, UGTs offer protection from external damage but require proper corrosion protection and regular inspections.
- Horizontal vs. Vertical Tanks: Horizontal tanks are ideal for transport and portability, while vertical tanks save ground space and are often used in stationary setups.
- Double-Wall Tanks: These tanks offer an additional layer of protection against leaks, making them ideal for sensitive environments where spill prevention is crucial.
Materials Used in 1000 Gallon Fuel Tanks
- Steel: Known for its strength and durability, steel tanks are often coated with anti-corrosion materials for longevity.
- Polyethylene (Plastic): Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, plastic tanks are suitable for specific fuel types but may lack the strength of steel.
- Fiberglass: Excellent corrosion resistance and suitable for underground use due to its non-corrosive properties.
Key Features and Specifications
A standard 1000 gallon fuel tank typically includes:
- Capacity: 1000 gallons
- Dimensions: Approximately 48 inches in diameter and 150 inches in length for horizontal tanks
- Material: Steel, polyethylene, or fiberglass
- Fill Ports: Secure fill points for fuel delivery
- Venting System: Prevents pressure build-up
- Gauges: Fuel level indicators
- Containment: Secondary containment for spill prevention (in double-wall models)
Applications of a 1000 Gallon Fuel Tank
- Agriculture: Storing fuel for tractors, combines, and other farm equipment
- Construction: Fueling heavy machinery on job sites
- Commercial Fleets: Fuel supply for company-owned vehicles
- Backup Generators: Powering large generators for industrial and residential use
- Aviation: Storing aviation fuel for small aircraft
Benefits of a 1000 Gallon Fuel Tank
- Bulk Fuel Storage: Reduces the need for frequent fuel deliveries
- Cost Savings: Buying fuel in bulk can lower costs per gallon
- Operational Efficiency: Ensures a steady fuel supply during critical operations
- Safety: Built-in containment and venting systems reduce spill risks
Regulations and Compliance
Proper installation and usage of a 1000 gallon fuel tank require adherence to safety standards and regulations, including:
- EPA Regulations: Compliance with spill prevention guidelines
- NFPA 30: Standards for flammable liquid storage
- Local Codes: Specific to regions and types of fuel stored
Maintenance and Safety Tips
- Regular Inspections: Check for corrosion, leaks, and structural integrity
- Cleaning: Periodic cleaning to remove sediment buildup
- Ventilation Checks: Ensure vents are functional
- Proper Labeling: Clearly label the tank with fuel type and safety instructions
- Training: Provide safety training for personnel handling fuel
Conclusion
A 1000 gallon fuel tank offers a practical fuel storage solution for various industries, ensuring safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. By selecting the appropriate type, material, and adhering to maintenance protocols, businesses can maximize the utility of their fuel storage while remaining compliant with safety standards.
also read this VanceAI Launches Revolutionary AI Video Enhancer: Video AI